ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities
BERT와 같은 PLM(Pretrained Language Model)들은 text에서 language information을 잘 파악할 수 있다.
하지만, knowledge information을 거의 고려하지 않는다는 문제점이 있다.
예를들면, 아래 그림에서 Blowin' in the wind, Chronicles: Volume One이라는 knowledge를 알지 못한 상태에서는 Bob Dylan이 Writer 또는 Songwirter라는 것을 인식하기 어렵다.
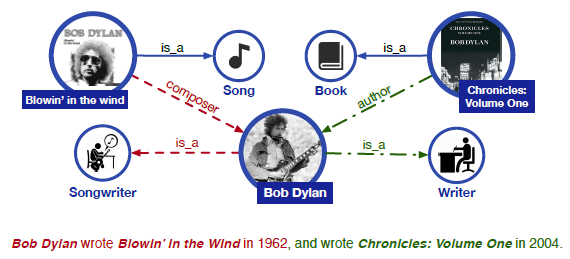
게다가, Bob Dylan이 Blowin' in the wind의 composer이고 Chronicles: Volume One의 author라는 relation을 파악하는 것도 어렵다.
이러한 문제들은 entity typing이나 relation classification 등의 task에서 큰 오류를 만들 수 있다.
본 연구에서는 외부의 knowledge들을 language information에 통합시키는 방법을 제안한다.
이러한 방법을 위해서는 2가지 과제가 있다.
-
Structured Knowledge Encoding
주어진 text들에 관련된 KB(Knowledge Base)의 knowledge들을 효율적으로 추출하고 encoding 해야 한다.
-
Heterogeneous Information Fusion
PLM이 text를 표현하는 방법과 knowledge를 encoding하는 방법은 상당히 다르다.
즉, 두 representation이 서로 다른 vector space상에 놓이게 된다.
따라서, 특별한 pretrain 방법을 통해서 knowledge information을 효율적으로 표현해야 한다.
Knowledge informatio을 추출하고 encoding하기 위해서 먼저, text상의 named entity를 파악한다.
그 후에, 각 named entity들에 대응되는 entity를 KB에서 찾는다.
KB의 entity는 TransE 논문에서 사용한 knowledge embedding 방법을 사용하여 encoding한다.
하나의 relation이 head와 tail 두 entity를 연결시킨다고 하면, 이 relationship은 embedding space상에서 entity간의 translation으로 간주한다.
즉, head의 embedding과 relation의 embedding을 더하면, embedding space상에서 tail의 embedding과 가까워지도록 학습을 시킨다.
이렇게 pretrain된 knowledge embedding 모델을 사용하여 KB에서 knowledge information을 추출한다.
본 연구에서는 BERT와 마찬가지로 MLM(Masked Language Modeling)과 NSP(Next Sentence Prediction) 방법으로 모델을 학습시킨다.
추가적으로, knowledge information을 효과적으로 학습하기 위해서 text와 KB 사이의 named entity의 연결을 masking하고, 이를 맞추는 방식의 학습을 진행한다.
이를 통해, 기존의 PLM들과는 다르게 knowledgeable language model을 학습시킬 수 있다.
Method
Model Architecture
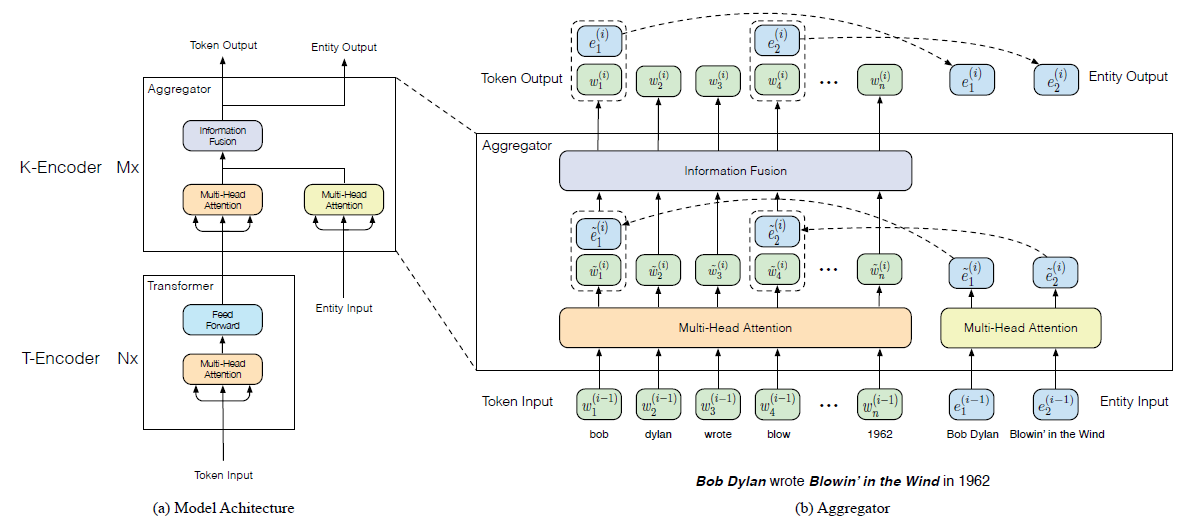
왼쪽의 그림은 모델의 전체적인 구조를, 오른쪽의 그림은 language information과 knowledge information을 합치는 aggregator를 자세하게 보여준다.
모델은 T-encoder(textual encoder)와 K-encoder(knowledgeable encoder)로 이루어진다.
T-encoder는 input token들로부터 language information을 계산하고, K-encoder는 T-encoder에서 계산한 representation과 각 token들에 대응되는 knowledge information을 합쳐 새로운 representation을 만든다.
T-encoder와 K-encoder의 layer 수를 각각 \(N,M\)이라고 하면, 먼저, T-encoder가 token embedding, segment embedding 그리고 positional embedding을 더해서 input embedding을 만든 후에, representation \(\{w_1,...,w_n\}\)을 계산한다.
여기서, T-encoder는 BERT와 동일한 구조를 가지며, \(w_i\)는 각 token들의 lexical, syntactic representation이 된다.
그 후, pretrain된 knowledge embedding 모델이 각 token들에 대응되는 entity들의 embedding, \(\{e_1,...,e_m\}\)을 계산한다.
Multi head attention이 T-encoder가 만든 representation과 pretrain 모델이 만든 embedding을 각각 새로운 represenation으로 만든다.
K-encoder는 아래와 같은 방법으로 각각 language information과 knowledge information을 의미하는 두 representation을 합쳐서 output을 계산한다.
\[\large\{\tilde{w}_1^{(i)},...,\tilde{w}_n^{(i)}\}=MHA(\{w_1^{(i-1)},...,w_n^{(i-1)}\})\\ \large\{\tilde{e}_1^{(i)},...,\tilde{e}_m^{(i)}\}=MHA(\{e_1^{(i-1)},...,e_m^{(i-1)}\})\\ \large h_j=\sigma(\tilde{W}_t^{(i)}\tilde{w}_j^{(i)}+\tilde{W}_e^{(i)}\tilde{e}_k^{(i)}+\tilde{b}^{(i)}),\: e_k=f(w_j)\\ \large w_j^{(i)}=\sigma(W_t^{(i)}h_j+b_t^{(i)})\\ \large e_k^{(i)}=\sigma(W_e^{(i)}h_j+b_e^{(i)})\]여기서 \(MHA\)는 multi head attention layer를 의미하며, \(\tilde{W}_t,\tilde{W}_e,W_t,W_e,\tilde{b},b_t,b_e\)는 학습되는 파라미터이다.
\(e_k=f(w_j)\)는 \(j\)번째 token과 KB상의 \(k\)번째 entity \(e_k\)가 대응되는 것을 의미한다.
만약 해당 token에 대응되는 entity가 없다면, 아래와 같이 계산한다.
\[\large h_j=\sigma(\tilde{W}_t^{(i)}\tilde{w}_j^{(i)}+\tilde{b}^{(i)})\\ \large w_j^{(i)}=\sigma(W_t^{(i)}h_j+b_t^{(i)})\]K-encoder의 가장 마지막 layer의 output \(\{w_1^o,...,w_n^o\},\{e_1^o,...,e_m^o\}\)이 모델의 최종 output이 된다.
Pretraining for injecting knowledge
Knowledge를 language information에 통합시키기 위해서, token과 entity 사이의 관계를 masking하고 예측하는 방법으로 pretraining을 진행한다.
KB에서 entity의 수는 매우 많을 수 있기 때문에, token에 대응되는 entity를 예측할 때는 주어진 entity들로만 softmax를 계산한다.
즉, \(\{w_1,...,w_n\}\)과 \(\{e_1,...,e_m\}\)을 입력 받으면 \(p(e_j\mid w_i)=\large\frac{exp(linear(w_i^o)\cdot e_j)}{\sum_{k=1}^mexp(linear(w_i^o \cdot e_k))}\)로 entity의 확률을 계산한다.
Token과 entity의 관계에 오류가 있을 수 있다는 점을 고려해서, 다음과 같은 작업들을 수행한다.
-
주어진 token과 entity에 대해 5%는 다른 무작위 entity로 대체한다.
이를 통해, 모델은 token이 잘못된 entity와 연결되어 있는 오류를 수정하도록 학습된다.
-
15%는 masking을 한다.
이를 통해, 모델은 entity와 연결되어야 할 token이 어느 entity와도 연결되지 않는 오류를 수정하도록 학습된다.
-
나머지 경우는 그대로 진행한다.
이를 통해, 모델은 token과 entity의 information을 통합하도록 학습된다.
Pretraining task로는 BERT와 마찬가지로 MLM과 NSP를 사용하며, 추가로 token과 entity의 관계를 맞추는 task를 사용한다.
즉, 3개의 task에 대해 joint하게 학습을 진행한다.
Finetuning for specific tasks
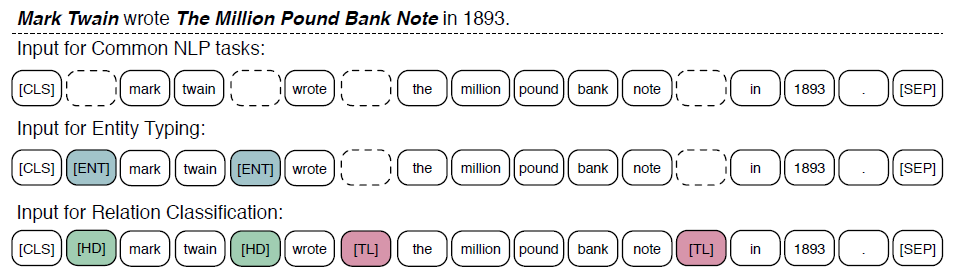
위의 그림은 finetuning시, input의 형태를 보여준다.
Finetuning은 BERT와 비슷한 방식으로 진행된다.
Sequence의 첫번째 token은 [CLS]이며, 이 token의 output은 sequence 전체의 representation이 된다.
Relation classification task에서는 [HD],[TL] 두 종류의 token을 추가하여 서로 연결되는 entity와 token을 표시해준다.
이 두 token들은 positional embedding과 비슷한 역할을 한다.
Entity typing task에서는 [ENT] token을 추가하여 KB에서 entity와 연결될 token을 표시해준다.
논문 링크
Preprint 2019
ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities

Leave a comment